Tax laws applicable to our country prescribe duties to be charged on goods and services on their import and export. Under the erstwhile/current indirect tax regime, excise tax, service tax, customs duty, VAT are all charges on the tax treatment of imports and exports. Under the GST regime, all these taxes have been subsumed into a single tax or the GST. The customs duty however will be continued to be levied additionally. In this article, we have highlighted the differences in the tax implications for exports and imports by drawing a comparison between the two regimes.
Current / Erstwhile Regime –
|
Description |
Example |
| Import of Goods |
- A countervailing duty or CVD at the rate equal to the rate of excise and a special additional duty or SAD at the rate equivalent to VAT is required to be paid on the import of goods.
- CVD and SAD imposed in order to bring the price of the product to the true market value in India.
- If the imported goods are used for further manufacturing of dutiable goods or provision of taxable services in India then the CVD paid can be availed as input tax credit; in case the importer is merely a trader, the input tax credit cannot be availed.
- SAD may be availed as a refund, conditionally.
- Customs duty is a cost the importer has to bear as no credit can be availed on it.
|
F&M Clothing based in Maharashtra purchases garments from Lara Fashion in Spain to a total value of INR 1,00,000. The customs duty is charged at 10%, CVD at 12.5% and the SAD at 4%. Therefore, the total cost of import will be the total value of the garments plus the total tax paid on the garments. |
| Import of Services |
- Upon importing a service into India, service tax needs to be paid on such service at the applicable rate. Tax credit can be claimed by an importer of services on the service tax so paid.
|
F&M Clothing based in Maharashtra hires designing services from Spain and the total value of the services is INR 5,00,000. The service tax is payable at 14%, additional taxes such as krishikalyancess and swachh bharat cess are at 0.5% each. The total cost of importing the service will thus be the cost of the service plus the added taxes. |
| Exports |
- Exports of goods and services is zero rated or at 0%.
- Tax refund may be claimed by an exporter on any inputs that are used for manufacturing, purchasing or providing the exported goods or services.
|
|

GST Regime –
|
Description |
Example |
| Import of Goods |
- Customs duty and IGST are the two taxes payable on goods that are imported (CVD and SAD are replaced by IGST).
- A full tax credit can be claimed as a refund of the IGST paid on import of goods, thus those that were earlier unable to claim the refund on CVD and SAD and now claim a full refund on imports.
- Customs duty remains a cost the importer has to bear as no credit can be availed on it.
|
F&M Clothing based in Maharashtra purchases garments from Lara Fashion in Spain for a total value of INR 1,00,000. The customs duty is charged at 10% and IGST at 18%. Therefore, the total cost of import will be the total value of the garments plus the total tax paid on the garments. |
| Import of Services |
- A supply is considered as a service import when the supplier is based / provides services from outside India and the recipient of the supply / place of supply is in India
|
F&M Clothing is based in Maharashtra (recipient) and it avails of designing services in Maharashtra (place of supply) from Lara Fashion in Spain (supplier). Here the total cost of the supply of the service will be the cost of the designing service plus the IGST at 18%. |
| Export |
- Exports of goods and services is zero rated or at 0%.
- Tax refund may be claimed by an exporter on any inputs that are used for manufacturing, purchasing or providing the exported goods or services.
|
|
| Export of Services |
- For a service to be considered as an export under the GST it must fulfil the following conditions – the place of location of the supplier of the service should be India; the place of location of recipient of the service and the supply of the service should be outside India; the payment in return for the supply provided must be received in convertible foreign exchange by the supplier and the supplier and the recipient must not be establishments part of the same person
|
|

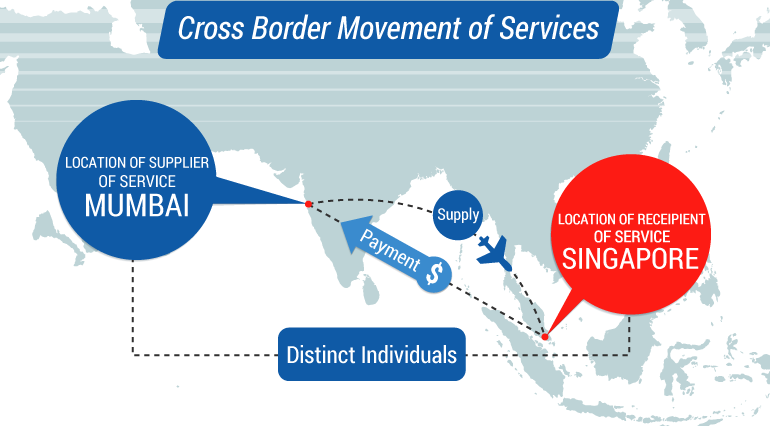
For example: Rohan Consultants in Mumbai, Maharashtra, provides business consultancy services to Abey’s Engineering in Singapore. The payment for the service has been received in Singapore Dollars.
Here,
Location of supplier: Mumbai, Maharashtra
Location of recipient: Singapore
Place of supply: Place of supply will be the location of the recipient, i.e. Singapore.
Payment for the service: Payment for the service has been received in convertible foreign exchange, i.e. Singapore Dollars.
Relationship between the supplier and recipient: The supplier and recipient are distinct persons.
Hence, this supply qualifies as an export of service. Rate of tax on the supply will be 0%.
The levy of taxes and treatment of taxes in case of imports and exports largely remain the same under GST in comparison with the existing laws. In case of an importer, full input credit will be available on the IGST paid on imports and additional input credit will be available on the GST paid on all types of inputs used or intended to be used in the course of or for the furtherance of business. Similarly, in the case of an exporter, refund will be given on the tax paid on all inputs used in the course of business. Overall, costs of import and export are expected to reduce under GST and compliance is expected to become easier with the convergence of multiple tax laws into one law.






